Psychological Relationship of Mechanical Ventilation Power on Mortality of Covid-19 Critically Ill Patients
Main Article Content
Abstract
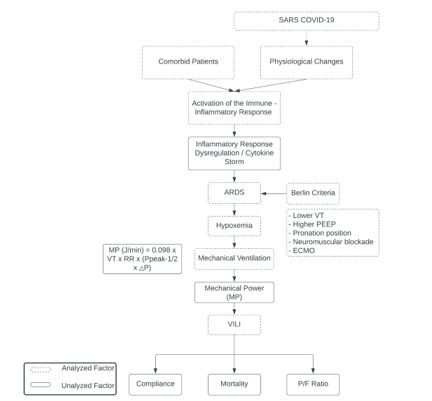
Introduction: ARDS is a type of lung injury that causes inflammation and makes it harder for oxygen to get into the bloodstream. Some treatments have been suggested, such as using less air with each breath, increasing pressure when breathing out, and using special positions or machines to help the lungs. But it's not clear how much these treatments can improve outcomes for patients with ARDS. So far, no studies have looked specifically at whether using more or less mechanical power to help patients breathe affects their chances of survival or other important measures of health.
Objectives: This research aimed to investigate how the use of mechanical ventilation affects the likelihood of death in patients who are severely ill with COVID-19.
Methods: This study adopts a cross-sectional design and retrospective analysis, observing critically ill patients who are being treated in the Special Isolation Ward of Dr. Soetomo Hospital's intensive care unit. The population for this study consists of critically ill patients who meet the inclusion and exclusion criteria. The research sample is obtained through randomized sampling, where all eligible individuals meeting the criteria are included in the sample size.
Results: The study findings reveal a correlation between mechanical ventilation power and mortality among COVID-19 patients with ARDS. The mechanical power of ventilation is identified as a significant variable in this study, with a cut-off point of 17.4. Patients above this cut-off point are at 3.65 times higher risk of death compared to those below it. Moreover, there is evidence of a relationship between the mechanical power of ventilation variable and the P/F Ratio, as a higher mechanical power is associated with a decrease in the P/F Ratio.
Conclusions: The study has identified a correlation between the P/F Ratio variable and mortality in COVID-19 patients with ARDS. On the other hand, there is no evidence of a relationship between the compliance variable and mortality in COVID-19 patients with ARDS.