Growth Trends in the Components of Money Stock in India: An Estimation by the Structural Stability Regression Model
Main Article Content
Abstract
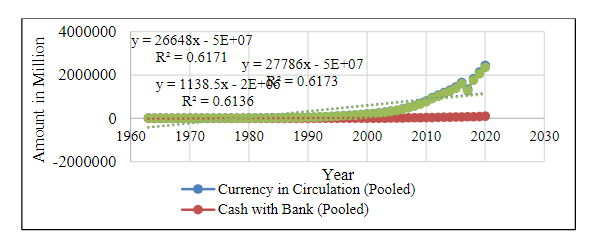
The expansion of the money supply is crucial for both achieving price stability in the economy and speeding up the process of economic development. The objectives are to evaluate the growth and alterations in the money stock's constituents and to assess the structural integrity of the money stock components in light of the new economic strategy. Data on money in circulation, cash in banks, money in the hands of the general public, other deposits with the RBI, bankers' deposits with the RBI, demand deposits, time deposits, reserve money, narrow money, and broad money were compiled using the Reserve Bank of India's handbook of statistics on the Indian economy for 2020–21. The data covered two distinct time periods associated with India's new economic policy: 1963–1991 and 1992–2020. Accordingly, the reserve, narrow, and broad money increased from 25460, 33170, and 45600 million in 1962–1963 to 30297070, 4125948, and 167999630 million in 2019–2020. Its growth rates were 118898.7, 12338.8, and 368320.2. The components of money stocks in India have all undergone structural changes as a result of the new economic strategy. The study also discovered that there are no negative growth rates for reserve money, narrow money, or broad money for the pre- and post-liberalised periods. Period II is much superior in terms of the compound annual growth rate of money stock components.