Turmeric with Its Curcumin as a Natural Lipid Lowering Nutritional Supplement in Subjects with Hyperlipidemia
Main Article Content
Abstract
Atherosclerosis represents one of the most problematic inflammatory consequences that predisposing to cardiovascular diseases. Although, statins listed on the top treatment of atherosclerosis cardiovascular disease (ASCVD), they possess several adverse effects like rhabdomyolysis, loss of cognition, and hepatic dysfunction.
The present study evaluates the role of natural turmeric (the rhizome of curcuma longa) in lowering plasma lipid in subjects with hyperlipidemia.
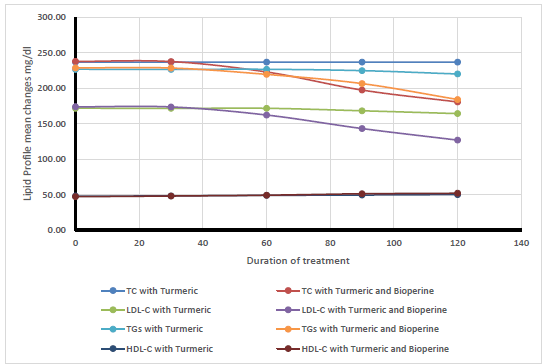
The study was performed on 60 subjects (age:23-46 years), (BMI: 26-33 kg/m²) diagnosed with hyperlipidemia, according to American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association guidelines and National Cholesterol Education Program. They were divided randomly into two equal groups, the 1st group were given 1500 mg turmeric per day in three divided doses before meal, and the 2nd group were given 1500 mg of turmeric with 10mg of bioperine thrice per day. All participants continued to take the prescribed regimen doses for 120 days, and the blood samplewere collected (13 hours of fasting time) at 0,30,60,90, and 120 days. The paired sample t-test was used to compare the changes in lipid profile of each group during the 120 days of herbal supplementation but independent t-test was used to compare changes between the two groups. P-value < 0.05 considered significant. The results showed that turmeric treated patients displayed a significant decrease in total cholesterol, LDL-C, and triglyceride (P < 0.001; 90 days of treatment) and a significant rise of HDL-C level (p.value< 0.001; 120 days of treatment). Nevertheless, The substantial decline in total cholesterol, LDL-C, and triglyceride p.value< 0.001 in patients in the second group who were given turmeric with bioperine began after 60 days of treatment, which was also the same length needed for significant elevation p.value< 0.001 of HDL-C.
Between the two comparison groups, there were no significant variations in anthropometric and clinical parameters. Furthermore, despite the fact that there were no significant differences p.value> 0.05 on day 0 in terms of (total cholesterol, LDL-C, HDL-C, and triglycerides), significant differences began to emerge after 60 days of treatment between the two comparative groups, in which total cholesterol, LDL-C, and triglycerides began to decrease significantly in subjects given turmeric with bioperine compared to subjects given turmeric without bioperine. In addition, there was no significant difference in HDL-C until 120 days of treatment, when HDL-C began to rise considerably in participants who took turmeric plus bioperine compared to those who took turmeric alone.
ASCVD is strongly associated with morbidity and mortality that required high attention to provide multiple save, effective, and well-tolerated therapy.Curcuma longa may meets the ambition, and can find in what looking for.
The study concluded that, turmeric the natural and well tolerates especially if it taken with bioperine may act as a better natural herbal supplement surrogate with lipid lowering performance.