Influence of Decentralization of the Smart Grid and Its Social & Economic Policy
Main Article Content
Abstract
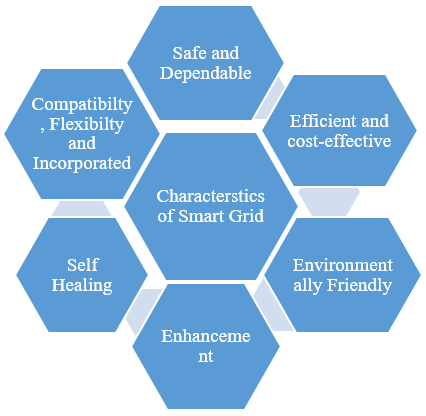
India is stubborn in meeting the fast-growing economy's electric power needs. The reorganization of the power industry merely adds to the many difficulties that power system engineers face. To deploy the Smart Grid (SG) at different levels in the Indian electricity systems, it is advised that a better automation mechanism be required. The idea of a "smart grid" seeks to improve the intelligence and effectiveness of grid operations. Operations on the smart grid are feasible with the correct deployment. It might provide new opportunities with substantial financial ramifications. This research may be found in a variety of Smart grid initiatives and its consequences for the expanding Indian power industry. This study suggests that the power flow controller for solar (PV), wind, and fuel cell generation systems be researched together. It is necessary for a conventional grid to be connected to solar, photovoltaic, fuel cell, three-phase inverter, battery units, wind energy, associated power electronics devices, and loads. This comprehensive model of photovoltaic and fuel cell connections to the smart grid starts with a PV source that is connected to a boost dc-dc converter, followed by a three phase inverter that supplies the smart grid with solar energy. A fuel cell is also connected to an inverter that supplies the smart grid with power. In order to adjust for voltage imbalances, harmonics, active power, and load voltage and current changes, this inverter is set up as a shunt active power filter (APF).