Association of Sleep Disorders and Mood State with Dopamine and Serotonin Levels in Alcoholism: A Psychological Comparative
Main Article Content
Abstract
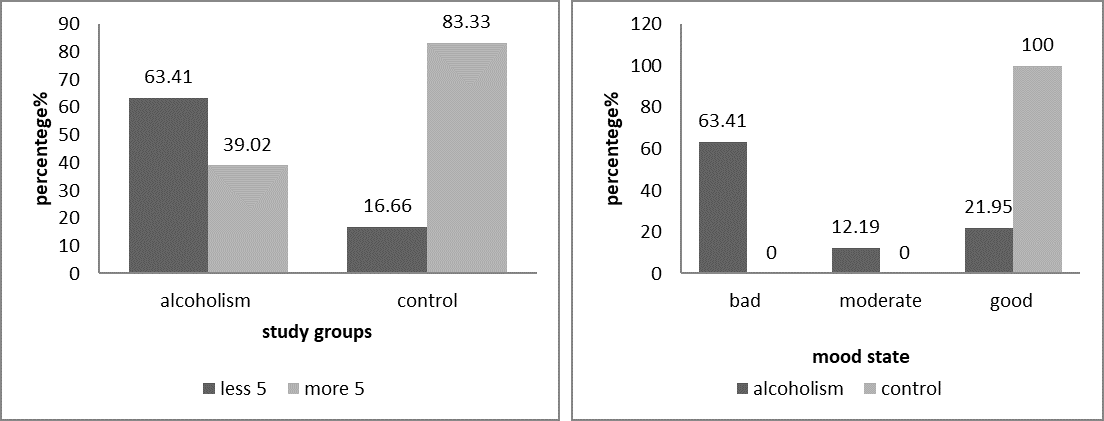
The sleep disorder and mood state is affected by different factors, alcoholism is one of the important problem contributed on different health disorders, present study aims to assessment of sleep disorders and mood state with dopamine and serotonin level in alcoholism, results show a significant reduction in age, sleep duration, serotonin and dopamine and significant elevation of BMI, the sleep duration less than 5 hours was high percentage in alcoholism (63.41%) and more than 5 hours was lower in alcoholism (16.66%). three categories of mood state including bad, moderate and good mood were had (63.41, 12.19, 21.95)% respectively. all control group was has good mood (100%), the dopamin level shows in less than 5 hour category non-sig differences reduction in alcoholism (p 0.555), while significant elevation in control group (p 0.035). the serotonin level shows in less than 5 hours category non-sig decresed in the alcoholism (p 0.647), and non-sig elevation in control group (p 0.525). The dopamine and serotonin levels according to mood state show significant differences (p 0.000) in dopamine level between mood state categories of alcoholism and control, but no significant differences within the alcoholism mood state categories, The serotonin level also shows significant differences among groups (p 0.005), its elevated in moderate mood of alcoholism and in good mood of control group, The correlation coefficient between dopamine and sleep duration was non-significant weak positive correlation (r 0.069, p 0.666), while in control group significant inverse correlation (r -.383, p 0.037). The correlation coefficient between serotonin and sleep duration shows non-significant weak positive association (r 0.016, p 0.921) in alcoholism group and in control group non-significant inverse correlation (r -0.279, p 0.135), the sleep time according to mood state shows non-significant differences in alcoholism mood state categories and significant with control group, Current finding concluded that the reduction in dopamine and serotonin reduction in alcoholism may be effected in the sleep duration and mood state
Article Details
References
Krueger, P. M. & Friedman, E. M. Sleep duration in the United States: a cross-sectional population-based study. Am J Epi. 169, 1052–1063 (2009).Return to ref 1 in article
Cappuccio, F. P., D’Elia, I., Strazzullo, P. & Miller, M. A. Sleep duration and all-cause mortality. A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. Sleep 33, 585–592 (2010).
Shan, Z. et al. Sleep duration and risk of type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of prospective studies. Diabetes Care 38, 529–37 (2015).
Palagini, L., Bruno, R. M., Gemignani, A., Ghiadoni, L. & Riemann, D. Sleep loss and hypertension: a systematic review. Curr Pharm Des. 19, 2409–19 (2013).
Ouzounakis P, Iliadis C, Monios A, Kourkouta L. Sleep-disordered breathing. Journal of Recent Trends in Engineering & Research (IJRTER). 2016;2(3):161-165.
Roehrs, T., Papineau, K., Rosenthal, L. & Roth, T. Ethanol as a hypnotic in insomniacs: Self administration and effects on sleep and mood. Neuropsychopharmacology 20, 279–286 (1999).
Stein, D. & Friedmann, P. D. Disturbed sleep and its relationship to alcohol use. Subs. Abuse 26, 1–13 (2005).
Chakravorty, S., Chaudhary, N. S. & Brower, K. J. Alcohol dependence and its relationship with insomnia and other sleep disorders. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 40, 2271–2282 (2016).
Colrain, I. M., Nicholas, C. L. & Baker, F. C. Alcohol and sleeping brain. Handb Clin Neurol. 125, 415–431 (2014).
Jacobs BL, Azmitia EC Structure and function of the brain serotonin system. Physiological Reviews. 1992;72(1):165-229.
Chiara M Portas, Bjørn Bjorvatn, Reidun Ursin, Serotonin and the sleep/wake cycle: special emphasis on microdialysis studies, Progress in Neurobiology, Volume 60, Issue 1, 2000, Pages 13-35, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-0082(98)00097-5.
Dopamine: Biological Activity. IUPHAR/BPS Guide to Pharmacology. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. Retrieved 29 January 2016.
Dissecting components of reward: ‘Liking’, ‘wanting’, and learning. Current Opinion in Pharmacology. 2009;9(1):65-73. PMC 2756052.
Banerjee N. (2014). Neurotransmitters in alcoholism: A review of neurobiological and genetic studies. Indian journal of human genetics, 20(1), 20–31. https://doi.org/10.4103/0971-6866.132750.
Volkow ND, Wang GJ, Telang F, Fowler JS, Logan J, Jayne M, et al. Profound decreases in dopamine release in striatum in detoxified alcoholics: Possible orbitofrontal involvement. J Neurosci. 2007;27:12700–6. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar].
Virkkunen M, Linnoila M. Serotonin in early onset, male alcoholics with violent behaviour. Ann Med. 1990;22:327–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar].
Ahmed Cherif Megri, Sameer Hamoush, Ismail Zayd Megri, Yao Yu. (2021). Advanced Manufacturing Online STEM Education Pipeline for Early-College and High School Students. Journal of Online Engineering Education, 12(2), 01–06. Retrieved from http://onlineengineeringeducation.com/index.php/joee/article/view/47
Yan QS. Extracellular dopamine and serotonin after ethanol monitored with 5-minute microdialysis. Alcohol. 1999;19(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/S0741-8329(99)00006-3. [PubMed] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
Yim HJ, Gonzales RA. Ethanol-induced increases in dopamine extracellular concentration in rat nucleus accumbens are accounted for by increased release and not uptake inhibition. Alcohol. 2000;22(2):107–115. doi: 10.1097/01.ALC.0000075825.14331.65. [PubMed] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
Yoshimoto K, McBride WJ, Lumeng L, Li TK. Alcohol stimulates the release of dopamine and serotonin in the nucleus accumbens. Alcohol. 1992;9(1):17–22. doi: 10.1016/0741-8329(92)90004-T. [PubMed] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
Yim HJ, Schallert T, Randall PK, Gonzales RA. Comparison of local and systemic ethanol effects on extracellular dopamine concentration in rat nucleus accumbens by microdialysis. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1998;22(2):367–374. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1998.tb03662.x. [PubMed] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar].
Yim HJ, Robinson DL, White ML, Jaworski JN, Randall PK, Lancaster FE, et al. Dissociation between the time course of ethanol and extracellular dopamine concentrations in the nucleus accumbens after a single intraperitoneal injection. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2000;24(6):781–788. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Cowen MS, Lawrence AJ. The role of opioid-dopamine interactions in the induction and maintenance of ethanol consumption. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 1999;23(7):1171–1212. doi: 10.1016/S0278-5846(99)00060-3. [PubMed] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
Spanagel R, Herz A, Shippenberg TS. Opposing tonically active endogenous opioid systems modulate the mesolimbic dopaminergic pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1992;89(6):2046–2050. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Adermark L, Clarke RB, Olsson T, Hansson E, Soderpalm B, Ericson M. Implications for glycine receptors and astrocytes in ethanol-induced elevation of dopamine levels in the nucleus accumbens. Addict Biol. 2011;16(1):43–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1369-1600.2010.00206.x. [PubMed] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
Lovinger D. M. (1997). Serotonin's role in alcohol's effects on the brain. Alcohol health and research world, 21(2), 114–120.
Obermeyer W, Benca R. In: Aldrich M, editor. Effects of Drugs on Sleep in Neurology Clinics, vol. 14(3). Philadelphia: WB Saunders Co.; 1996. pp. 827-840
Colrain, I. M., Nicholas, C. L., & Baker, F. C. (2014). Alcohol and the sleeping brain. Handbook of clinical neurology, 125, 415–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-62619-6.00024-0
Stein, M. D., & Friedmann, P. D. (2005). Disturbed sleep and its relationship to alcohol use. Substance abuse, 26(1), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1300/j465v26n01_01
Cooper ML, Frone MR, Russell M, Mudar P. Drinking to regulate positive and negative emotions: A motivational model of alcohol use. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 1995;69(5):990–1005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar].
Schroder, K. E., & Perrine, M. W. (2007). Covariations of emotional states and alcohol consumption: evidence from 2 years of daily data collection. Social science & medicine (1982), 65(12), 2588–2602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2007.07.011.
Dugovic C. Role of serotonin in sleep mechanisms. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2001 Nov;157(11 Pt 2):S16-9. PMID: 11924032.
Monti JM, Jantos H. The roles of dopamine and serotonin, and of their receptors, in regulating sleep and waking. Prog Brain Res. 2008;172:625-46. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)00929-1. PMID: 18772053.
Lin L, Faraco J, Li R, Kadotani H, Rogers W, Lin X, Qiu X, de Jong PJ, Nishino S, Mignot E The sleep disorder canine narcolepsy is caused by a mutation in the hypocretin (orexin) receptor 2 gene. Cell 98:365–376.
Hobson JA, Stickgold R, Pace-Schott EF1998) ) The neuropsychology of REM sleep dreaming. NeuroReport 9:R1–R14.
John J, Wu MF, Boehmer LN, Siegel JM (2004) Cataplexy-active neurons in the hypothalamus: implications for the role of histamine in sleep and waking behavior. Neuron 42:619–634.
Aston-Jones G, Bloom FE (1981) Activity of norepinephrine-containing locus coeruleus neurons in behaving rats anticipates fluctuations in the sleep-waking cycle. J Neurosci 1:876–886.
Espana RA, Scammell TEز Sleep neurobiology for the clinician. Sleep 27:811–820.
Baixauli E (2017) Happiness: Role of Dopamine and Serotonin on Mood and Negative Emotions. Emerg Med (Los Angel) 7: 350. doi:
4172/2165-7548.1000350
Maas J. W., Bowden C. L., Miller A. L., et al. Schizophrenia, psychosis, and cerebral spinal fluid homovanillic acid concentrations. Schizophrenia Bulletin. 1997;23(1):147–154. doi: 10.1093/schbul/23.1.147. [PubMed] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
Juárez Olguín, H., Calderón Guzmán, D., Hernández García, E., & Barragán Mejía, G. (2016). The Role of Dopamine and Its Dysfunction as a Consequence of Oxidative Stress. Oxidative medicine and cellular longevity, 2016, 9730467. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/9730467.
Ma, H., & Zhu, G. (2014). The dopamine system and alcohol dependence. Shanghai archives of psychiatry, 26(2), 61–68. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1002-0829.2014.02.002.
Sari, Y., Johnson, V. R., & Weedman, J. M. (2011). Role of the serotonergic system in alcohol dependence: from animal models to clinics. Progress in molecular biology and translational science, 98, 401–443. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-385506-0.00010-7
Palagan Senopati Sewoyo, Anak Agung Ayu Mirah Adi, Ni Luh Eka Setiasih, I Gusti Ayu Mirah Afsari Dewi. (2022). Haematological Profile of Rat Fibrosarcoma Models After Virulent Newcastle Disease Virus Virotherapy: A Pilot Study. Revista Electronica De Veterinaria, 47 - 55. Retrieved from https://www.veterinaria.org/index.php/REDVET/article/view/138
Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Sleep Medicine and Research; Colten HR, Altevogt BM, editors. Sleep Disorders and Sleep Deprivation: An Unmet Public Health Problem. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 2006. 3, Extent and Health Consequences of Chronic Sleep Loss and Sleep Disorders. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK19961/
Brandt R, Bevilacqua GG, Andrade A. Perceived Sleep Quality, Mood States, and Their Relationship With Performance Among Brazilian Elite Athletes During a Competitive Period. J Strength Cond Res. 2017 Apr;31(4):1033-1039. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000001551. PMID: 28328717.
Al-Terehi, Mona N, Zahraa Haleem Alqaim and Arafat Hussein Aldujaili. “Impact of DNA Repair System Genes RAD-18 and XRCC1 Polymorphism in Depression Disorders Patients.” Clin Schizophr Relat Psychoses 15(2021).
Al-Terehi MN, Altimari US, Kadhim AJ, Al-Rrubaei HA. The Combination Between Anti-depressant and Anti-diabetic Therapy Effects in Depressed Patients with Type 2 Diabetic Mellitus. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance. 2021;12(4):287-289.